Compare PDF annotation formats: XFDF and Instant JSON
In addition to reading and writing annotations embedded into a PDF, Nutrient Java SDK enables you to use external files to manage annotations.
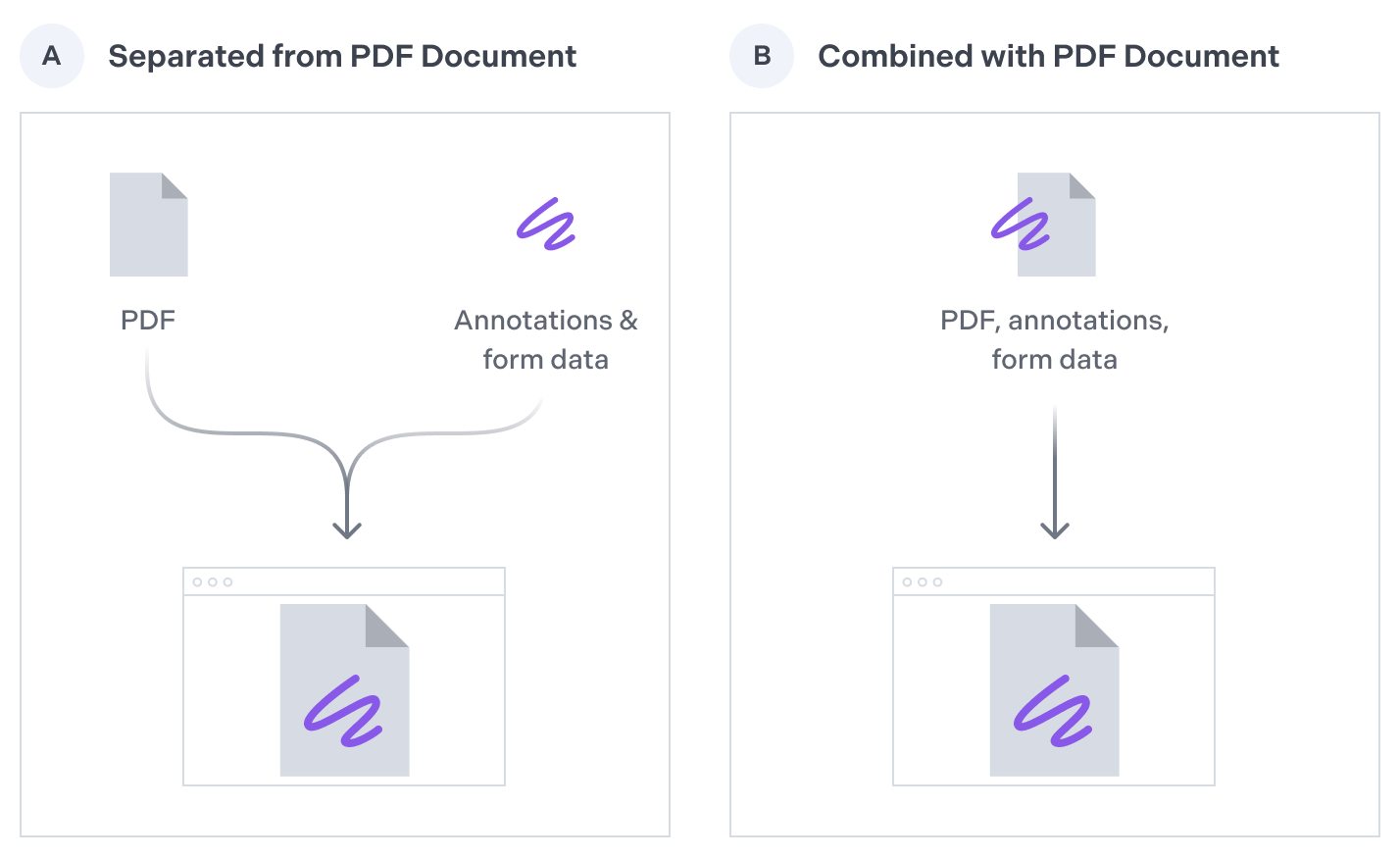
Nutrient Java SDK supports reading and writing annotations in the following external data file formats:
-
XML Forms Data Format (XFDF)
-
Instant JSON
For most use cases, we recommend Instant JSON because, unlike XFDF, it can store deleted annotations. It also has built-in support for comparing (diffing) changes to annotations. This makes it ideal for synchronizing annotations to a server, or across users, devices, or sessions. Instant JSON can be converted to XFDF. XFDF is best suited for importing data into the system or exporting it for integration with third-party PDF applications.
Comparing data formats
| Criteria | XFDF | Instant JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Compatible with third-party PDF applications | ✓ | * |
| ISO-standard format | ✓ | |
| Built-in support for comparing changes | ✓ | |
| Can store deleted annotations | ✓ | |
| Syntax | Verbose | Minimal |
| File size | Larger | Compact |
| Fully documented | ✓ | ✓ |
* Can be converted to XFDF for use in third-party applications.
XML Forms Data Format (XFDF)
Nutrient Java SDK has full support for reading and writing XFDF.
XFDF is an XML-based standard from Adobe XFDF (ISO 19444-1:2016) for encoding annotations and form field values. It’s compatible with Adobe Acrobat and many other third-party PDF applications.
XFDF is a representation of all annotation and form data inside a PDF document at a point in time. It doesn’t have a concept of differentials (diffs) for managing changes made by multiple users annotating the same PDF simultaneously, and it cannot store deleted annotations. This makes XFDF a challenging format to use for comparing changes, managing conflicts, and synchronizing annotations across users, devices, or sessions.
Instant JSON
Instant JSON is a format we created for bringing annotations and bookmarks into a modern format while keeping all important properties to make the Instant JSON spec work with PDF. It’s not directly supported by other frameworks; however, it can be converted to XFDF to make it interoperable.
Instant JSON is fully documented and supports persistent storage. It’s designed for synchronizing annotations to a server, and across users, devices, or sessions.