Audit trail: Track every action and stay compliance-ready
Table of contents

Try Workflow Automation free for 14 days
An audit trail is a chronological record of who did what, when, and why within a business process. Nutrient Workflow automatically captures every action, approval, and change — giving you complete visibility and compliance-ready documentation.
An audit trail tracks and records all tasks, activities, participants, timestamps, and actions within a workflow or business process. This documentation provides verifiable evidence that processes were followed correctly and helps identify errors when they occur.
Without a proper audit trail system, preparing for audits means searching through emails, tracking down signed documents, and contacting coworkers. According to McKinsey(opens in a new tab), nearly 20 percent of employee time is spent searching for information. Automated audit trails eliminate this waste.
What is included in an audit trail?
Audit logs trace every activity back to its source. For example, if a finance director approved a purchase, you can find out:
- When the approval was made (date and time)
- What files or data the approver reviewed
- Where the request originated
- What steps led up to the approval
- Who else was involved in the process
- What comments or notes were added
Nutrient Workflow captures all activity related to a process, including time/date, username, tasks performed, and related documents. You can view this information onscreen or export it to CSV for external reporting.
Benefits of audit trails
Automated audit trails provide measurable benefits across compliance, security, efficiency, and continuous improvement.
Compliance and audit readiness
Audit readiness is a priority in regulated industries. Automated audit trails log every action related to financial processes — what happened, when it happened, and who did it. This detailed record ensures you can quickly provide any documentation auditors request.
“Before Nutrient Workflow, we used paper ‘finance memos’ that weren’t all standard, that resulted in storage issues, that were often lacking the appropriate approvals, and then later were difficult to look up and locate. Our users always had trouble finding the information before, but now employees know where to find it; it’s all in one place.”
— Elizabeth Petrie, Capital Planning Controller, BP (Read case study)
Fraud protection
Manual processes create opportunities for fraud. One employee controlling an entire process from start to finish increases risk. Automated audit trails help by:
- Segregating duties — No single person can create and approve transactions.
- Enforcing approval thresholds — Higher-value transactions require additional approvals.
- Flagging suspicious activity — Automated systems identify unusual transactions for review.
- Creating tamper-proof records — Electronic signatures are linked to process records and cannot be altered.
Faster approvals with full visibility
Tracking approvals through email and paper documents is slow and error-prone. With automated audit trails, anyone with proper access can see exactly where a request is in the process — what tasks have been completed and what tasks are ahead. Alerts notify approvers when their attention is needed, and escalations route approvals to alternates when someone is unavailable.
Process improvement
Audit data reveals where processes break down. If you see repeated mistakes or delays, you can identify which forms, routing rules, or instructions need fixing. Historical records help you track improvement over time.
Audit trail example
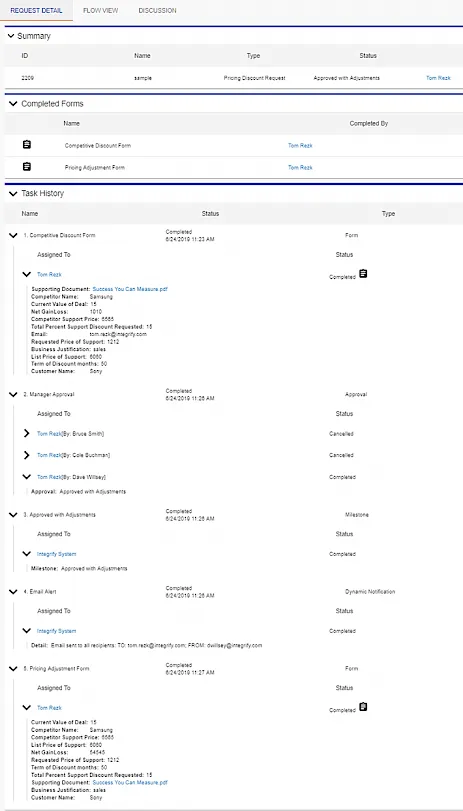
The screenshot below shows an audit trail from Nutrient Workflow. The Request Detail view is configurable; administrators can show or hide summaries, KPIs, tasks, forms, and reports.
This example shows a Competitive Discount Request marked “Approved with Adjustments.”
The screenshot shows two completed forms by Tom Rezk:
- Task History — Shows when the form was submitted, who submitted it, and what data was captured.
- Manager Approval — This request was assigned to a group of managers. Dave Willsey approved it, which automatically canceled tasks for the other managers.
- Pricing Adjustment — The manager approved with adjustments and completed a Pricing Adjustment Form. A notification was sent to the requester with the new pricing.
- Attachments — Any documents attached to the form appear with the form data.
Regulatory compliance requirements
Industries like healthcare, finance, government contracting, and insurance face regulatory audits. Audit trails prove you followed required standards. The following table shows common regulations that require audit trails.
| Regulation | Industry | What it requires |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA(opens in a new tab) | Healthcare | Track access to patient health information |
| SOX(opens in a new tab) | Public companies | Document financial controls and approvals |
| GDPR(opens in a new tab) | Any with EU data | Log data access and processing activities |
| FINRA(opens in a new tab) | Financial services | Record securities transactions and communications |
| 21 CFR Part 11(opens in a new tab) | FDA-regulated | Electronic signatures with tamper-proof audit trails |
FDA compliance (21 CFR Part 11)
Nutrient Workflow meets FDA requirements for electronic records and signatures. The system:
- Generates accurate, complete copies of records in human-readable and electronic form
- Limits system access to authorized individuals with role-based permissions
- Employs secure, computer-generated date/timestamped audit trails
- Enforces required steps and sequencing so key steps cannot be bypassed
- Links electronic signatures to records so they cannot be excised or copied
See the full 21 CFR Part 11 compliance overview.
How audit trails work in Nutrient Workflow
Nutrient Workflow automatically tracks every action in a process:
- Request submission — Web-based forms capture the initial request with all required data and attachments. Forms are accessible 24/7 through a branded portal.
- Routing and approvals — Requests route automatically based on business rules. The system logs each routing decision and approval.
- Collaboration — Stakeholders share information and files through a messaging panel. All communication is captured for audit.
- Reporting — Every request generates a complete audit trail. Export data to CSV or PDF for external reporting.
Get started with Nutrient Workflow
Nutrient Workflow automatically generates audit trails for every process. Start a free trial or request a demo to see audit tracking in action.
Related resources
- Avoiding audit traps
- Finance workflow automation: Approvals and audits
- Approval tracking software
- Security incident reporting
FAQ
An audit trail is a chronological record of who did what, when, and why within a business process. It tracks actions, participants, timestamps, and outcomes.
Nutrient Workflow automatically logs every action, approval, form submission, and status change. No manual documentation is required.
Audit trails capture who performed each action, when it occurred, what data was submitted, which files were attached, and what decisions were made.
Finance, healthcare, government, insurance, and any organization subject to regulatory compliance (SOX, HIPAA, GDPR, FINRA) benefit from audit trails.
Yes. Nutrient Workflow lets administrators configure which data appears in audit reports, including task history, forms, KPIs, and related requests.