Electronic signatures in a PDF
Table of contents

PDF documents are the accepted standard for legally binding documents in a digital format. PDFs are used to record major real estate deals, hire new employees, submit tax filings, and confirm payment for orders. For a user to make a purchase, verify their identification, or confirm a receipt, developers are faced with a decision: Which type of electronic signature is needed?
This article is not legal advice. If you have legal questions about electronic signatures or digital signatures, you should contact an attorney in your jurisdiction..
Why and when is an electronic signature needed?
Many countries have laws about what types of contracts require a signature(opens in a new tab). These can include land sales, long-term agreements, or purchases of goods above a certain cost. More broadly, a person’s signature is often used in a transaction to provide a sense of formality and confidence that the person signing “meant to do what they did,” and to create a reliable record of the transaction.
For centuries, pen (or quill!) and ink signatures were the accepted standard for confirming written agreements. At the beginning of the 21st century, many countries passed laws expressly recognizing the use of electronic records and electronic signatures to form legally binding, reliable contracts Electronic Identification and Trust Services (eIDAS(opens in a new tab) in the EU; Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) and Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act ESIGN(opens in a new tab) in the US; Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act PIPEDA(opens in a new tab) in Canada; IT Act(opens in a new tab) in India). Article 3 of eIDAS(opens in a new tab) defines an electronic signature as “data in electronic form which is attached to or logically associated with other data in electronic form and which is used by the signatory to sign.”
Software developers have come up with many different ways to confirm and verify a user’s intended action: button clicks, check boxes, freehand electronic signatures or initials, and unique embedded digital certificates, just to name a few. The Nutrient framework provides developers with their choice of the two most popular signature options: “ink” electronic signatures, and certificate-based PDF digital signatures.
Option 1: “Ink” electronic signatures
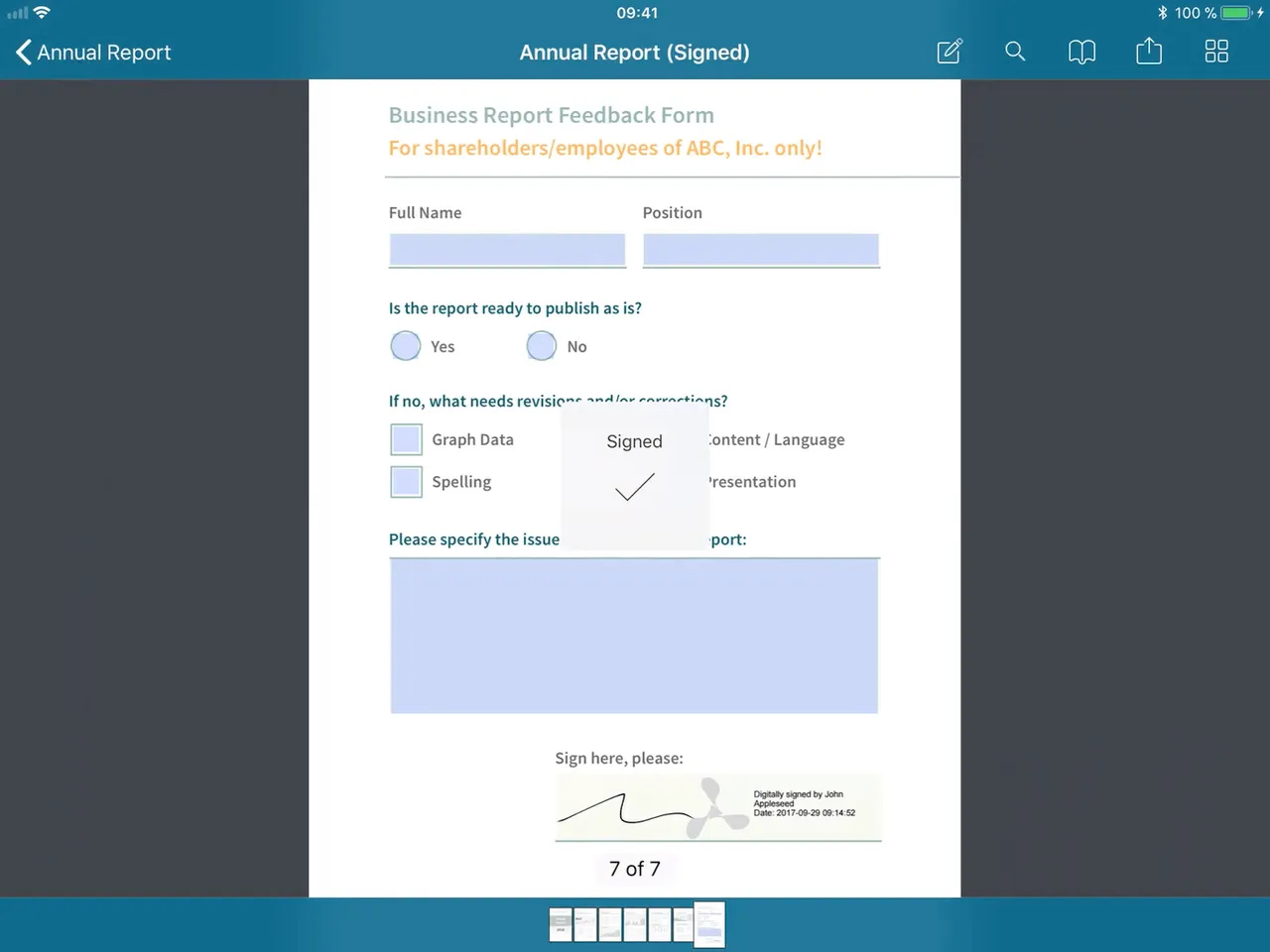
Ink eSignatures involve the user creating a freehand ink annotation using their fingertip, stylus, or mouse. Our Electronic Signatures component supports this input method, along with ability to generate eSignatures from text and scanned images. Electronic Signatures can be stored for repeated use.
Ink eSignatures are widely used in modern software solutions. Users can electronically sign forms and contracts, initial document margins to confirm the content, and establish a record that an action was taken as intended. At Nutrient, we provide a user-friendly electronic signature sdk for PDFs across multiple platforms, as shown below.
iOS
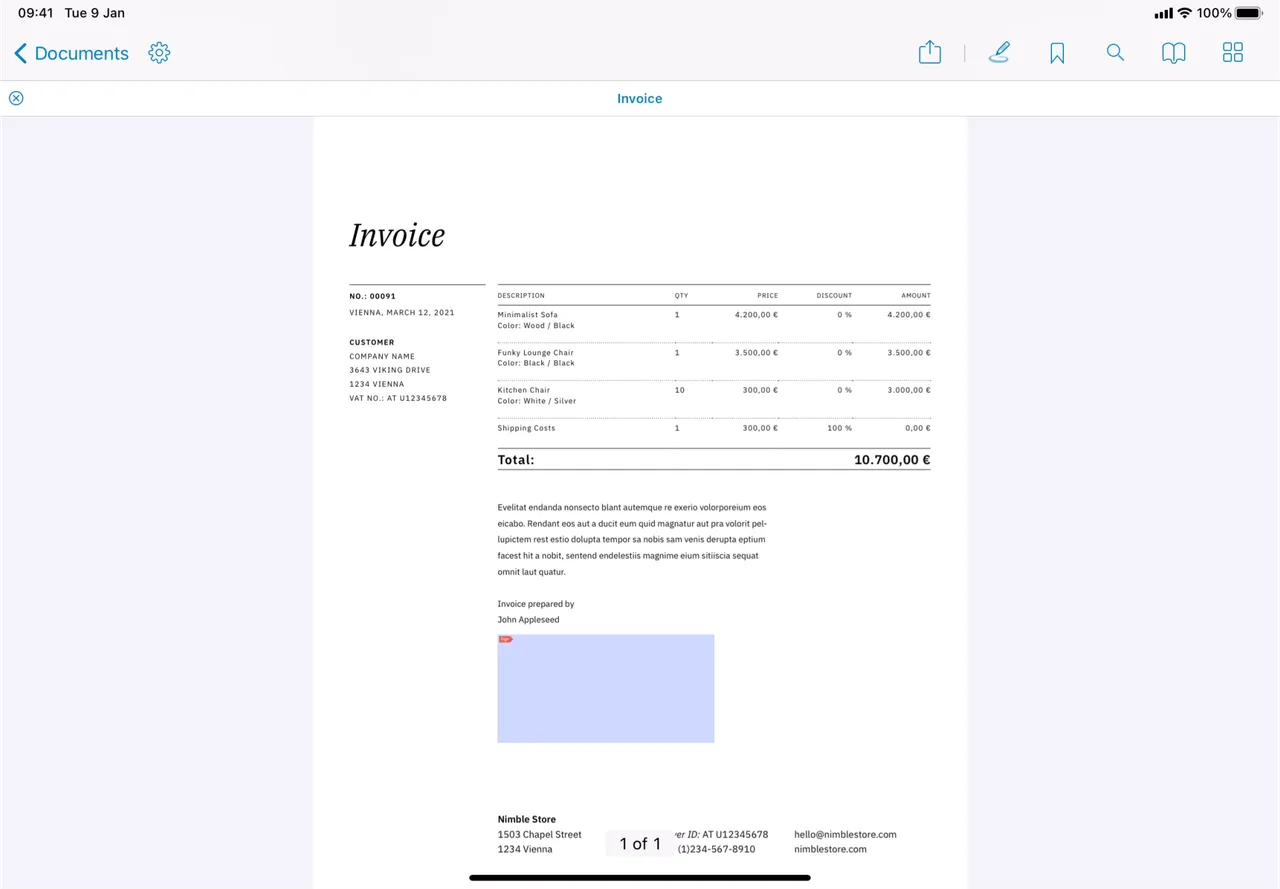
Web
Many countries have adopted laws that make ink eSignatures on digital documents legally equivalent to traditional pen-and-ink signatures on physical paper. For example, the ESIGN Act in the US provides that an eSignature is valid as long as:
- The party consents to using an electronic record;
- The party intends to sign the record;
- The party’s signature is attached to or associated with the record; and
- The record is retained and can be produced if requested.
Even if you don’t plan to distribute your app in the US, these elements can be a helpful guideline when including ink electronic signature functionality in your product. Our Nutrient framework makes it easy to add and store electronic signatures in a PDF either via our built-in UI or programmatically through the API.
Enable users to sign documents with freehand ink signatures across iOS, Android, and Web using Nutrient’s SDKs.
Option 2: Certificate-based digital signatures
A digital signature is an algorithm and encryption scheme that establishes the authenticity of a digital document. Essentially, a digital signature acts as a fingerprint that is unique to each user. It verifies the signer’s identity, ensures the signer cannot deny having signed the record, and confirms that the record was not altered in transit. PDF Digital Signature usage is increasing in popularity across many different software categories, and although it was originally utilized only in formal, complex legal contracts and banking transactions, the ease of use and decreasing cost barriers to PDF digital signatures are resulting in a much wider utilization of this more secure option.
The PDF specification(opens in a new tab) provides for creation and verification of cryptographically-secure digital signatures through public key infrastructure (PKI), which provides a secure and reliable system of managing and exchanging digital certificates. This system uses a hashing algorithm to generate two long numerical keys: one public and one private. The signing party’s private key is used to create and encrypt a PDF Digital Signature hash when the PDF is signed, and the hash matches the electronically signed PDF. Often, the digital signature is marked with additional metadata, such as the date and time of the digital signature, the IP address, the speed of signing, and biometric data like method of input, pressure sensitivity, and touch radius.
To ensure that both the document and the keys are valid and secure, third-party organizations called certificate authorities (CAs)(opens in a new tab) issue digital certificates and ensure key security. CAs are vetted and approved by government regulators and/or are accepted within certain industries. The issued certificate includes the public key for a digital signature and confirms that the key belongs to the signing party. CAs issue time-limited certificates. Both the signing party and the receiving/verifying party must use the same CA for a given PDF.
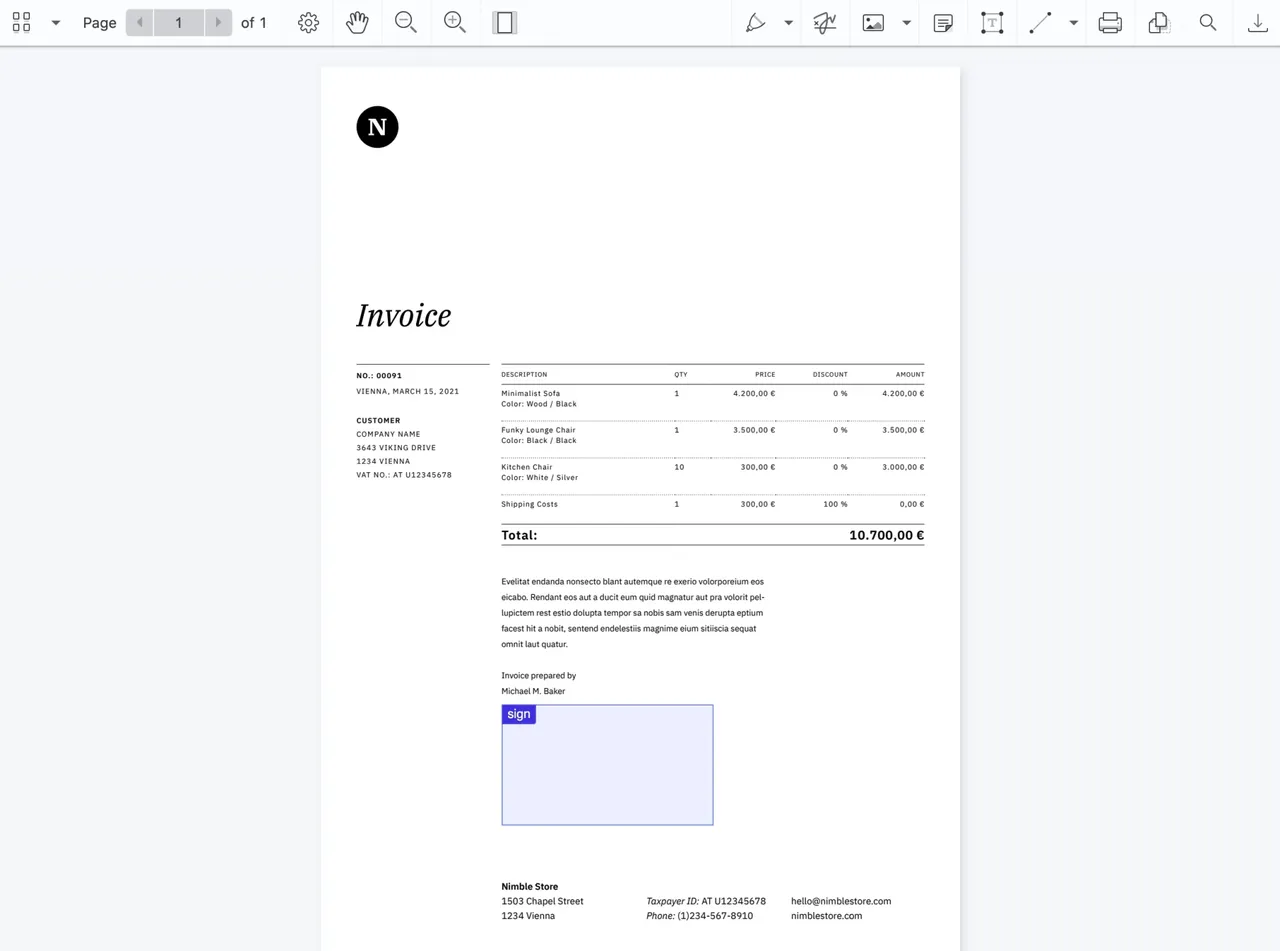
Within your app, a digital signature can be applied to a PDF by means of a registered user inputting an ink signature and password and uploading a certificate. Nutrient’s digital signature functionality is easy and intuitive for users — below is an example in iOS.
iOS
Nutrient supports the PDF 1.7/2.0 digital signature specification; RSA and ECDSA signing algorithms; and MD4, MD5, and SHA-2 (SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512-256) hashing algorithms.
Our PDF digital signature SDKs make it easy to add plug-and-play digital signature functionality into your app. Click here for a detailed walkthrough of how to integrate Nutrient’s Digital Signatures API.
Integrate certificate-based PDF digital signatures to ensure compliance and non-repudiation with Nutrient’s SDKs.
Option 3: Signatures in blood on musty parchment
As an alternative to ink eSignatures and digital signatures, this solution was predominantly used by highway thieves and pirates in the 18th century. It is highly disfavored in the modern era, and it is not supported by Nutrient frameworks. 😉
FAQ
There are two primary types of electronic signatures for PDFs: “ink” electronic signatures, and certificate-based PDF digital signatures. Ink eSignatures involve creating a freehand signature, while digital signatures use encryption to verify the signer’s identity and ensure document integrity.
Ink electronic signatures allow users to create a freehand signature using a fingertip, stylus, or mouse. These signatures can be stored for repeated use and are legally equivalent to traditional pen-and-ink signatures in many countries.
A certificate-based digital signature is an encrypted digital fingerprint unique to each user. It verifies the signer’s identity, ensures non-repudiation, and confirms that the document has not been altered. These signatures use a public key infrastructure (PKI) for security.
Various legal frameworks recognize electronic signatures, including the eIDAS regulation in the EU, the ESIGN Act and UETA in the US, PIPEDA in Canada, and the IT Act in India. These laws provide the legal basis for the use of electronic signatures in digital transactions.
Nutrient provides components for both ink and certificate-based digital signatures, making it easy to integrate electronic signature functionality into your app. Developers can use the built-in UI or programmatically add signatures through the API across multiple platforms like iOS, Android, and Web.
Conclusion
There are many reasons to require a user’s eSignature within your app. It is critical to understand the distinctions between ink electronic signatures and certificate-based PDF digital signatures when designing your document workflow, function, and backend.
For hand-drawn signatures and initialing, ink eSignatures are the right choice, and they’re easily implemented with our Electronic Signatures API. When unique, encrypted signature verification is required, use our PDF Digital Signatures API to ensure compliance and reliability.
Check out our detailed developer guides for iOS, Android, Web, and Windows for more information. Also, check out our simple to integrate REST Digital Signatures API. You can try all of our SDKs for free to see what works best for your app. When you’re ready to move forward, contact our Sales team for licensing and pricing information. And if you run into any issues, our developers are always available to answer questions and provide technical support!
Experiment with both electronic and digital signatures in your app without commitment.







