How to flatten a PDF using Python
Table of contents

Flatten PDF documents using our flatten PDF Python API. Create a free account, get API credentials, and implement flattening using the requests library. Merge all layers — including annotations, form fields, and signatures — into a single non-editable layer for printing and secure distribution.
In this post, you’ll learn how to programmatically flatten PDFs in Python using our flatten PDF Python API. With our API, you receive 200 credits with the free plan. Different operations on a document consume different amounts of credits, so the number of PDF documents you can generate may vary. All you need to do is create a free account(opens in a new tab) to get access to your API key.
Why flatten PDFs?
Flattening PDFs is essential for document workflows that require finalized, non-editable outputs. Common use cases include:
- Print preparation — Merge all layers — including annotations, form fields, and signatures — into a single layer to ensure printers render the complete document correctly.
- Secure distribution — Lock completed forms to prevent recipients from modifying submitted data.
- Archival compliance — Create immutable document versions for legal and regulatory requirements.
- Consistent rendering — Guarantee documents appear identical across all systems and PDF readers.
- Workflow automation — Process batches of documents programmatically as part of your backend infrastructure.
Nutrient DWS Processor API
Document flattening is just one of our 30+ PDF API tools. You can combine our flattening tool with other tools to create complex document processing workflows, such as:
- Converting MS Office files and images into PDFs and then flattening them
- Merging several documents and then flattening the resulting document
- Adding watermarks and signatures to a document and then flattening them
Once you create your account, you’ll be able to access all our PDF API tools.
Step 1 — Creating a free account on Nutrient
Go to our website(opens in a new tab). You’ll see the page below, where you can create your free account.
Once you’ve created your account, you’ll be welcomed by the page below, which shows an overview of your plan details.
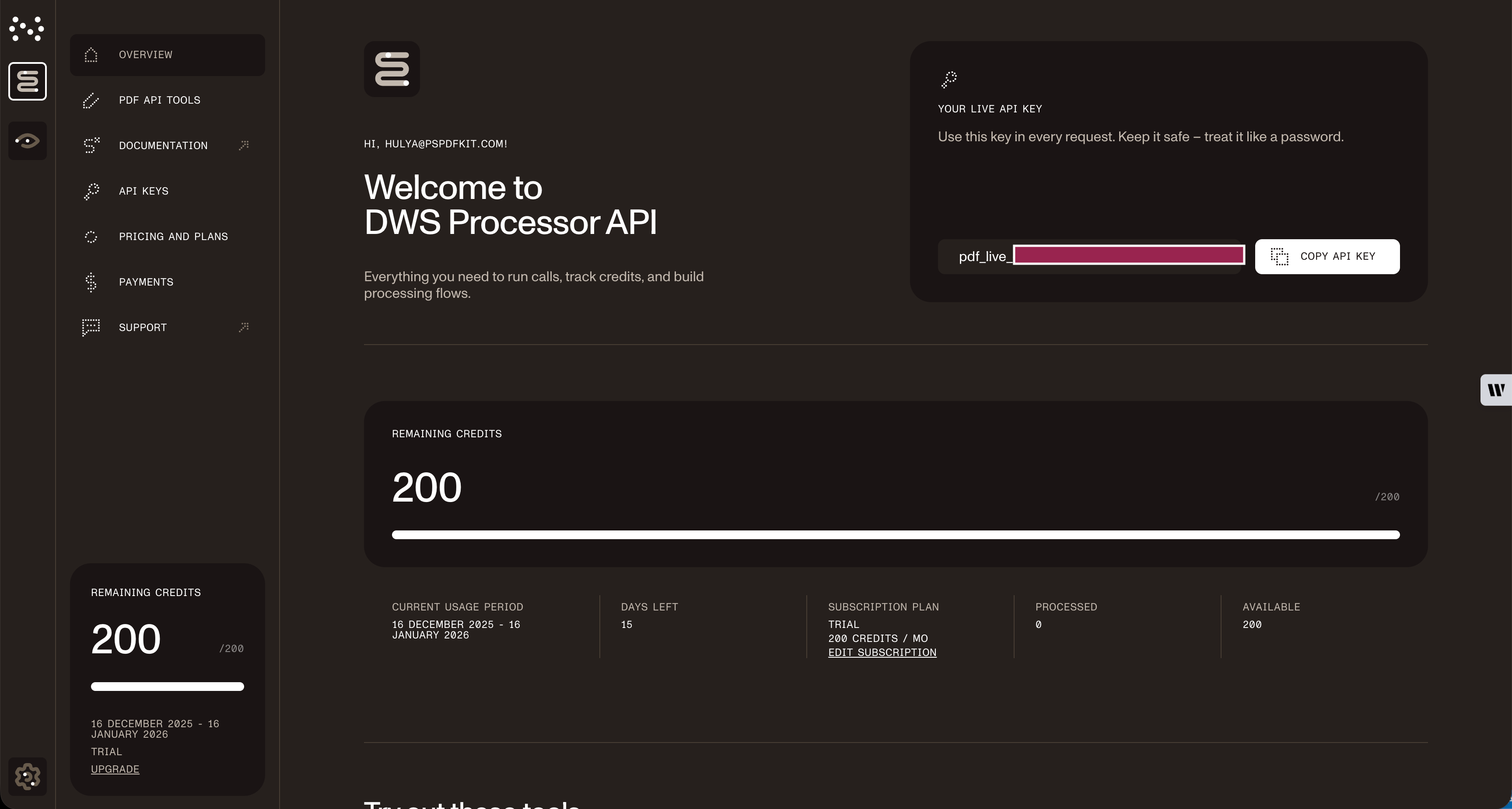
As you can see in the bottom-left corner, you’ll start with 200 credits to process, and you’ll be able to access all our PDF API tools.
Copy the API key, because you’ll need this for the flatten PDF API.
Step 2 — Setting up folders and files
Now, create a folder called flatten_pdf and open it in a code editor. For this tutorial, you’ll use VS Code as your code editor. Next, create two folders inside flatten_pdf and name them input_documents and processed_documents.
Then, in the root folder, flatten_pdf, create a file called processor.py. This is the file where you’ll keep your code.
Your folder structure will look like this:
flatten_pdf├── input_documents| └── document.pdf├── processed_documents└── processor.pyStep 3 — Writing the code
Assuming you already have Python installed, open the processor.py file in your code editor. Paste the code below into your file:
import requestsimport json
response = requests.request( 'POST', 'https://api.nutrient.io/build', headers = { 'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_API_KEY_HERE' }, files = { 'document': open('input_documents/document.pdf', 'rb') }, data = { 'instructions': json.dumps({ 'parts': [ { 'file': 'document' } ], 'actions': [ { 'type': 'flatten' } ] }) }, stream = True)
if response.ok: with open('processed_documents/result.pdf', 'wb') as fd: for chunk in response.iter_content(chunk_size=8096): fd.write(chunk)else: print(response.text) exit()Make sure to replace YOUR_API_KEY_HERE with your API key.
Code explanation
In the code above, you first import the requests and jsondependencies. After that, you create the instructions for the API call.
You then use the requests module to make the API call, and once it succeeds, you store the result in the processed_documents folder.
Output
To execute the code, use the command below:
python3 processor.pyAfter running the code, you’ll see a new processed file, result.pdf, located under the processed_documents folder.
The folder structure will look like this:
flatten_pdf├── input_documents| └── document.pdf├── processed_documents| └── result.pdf└── processor.pyConclusion
In this post, you learned how to flatten PDF files for your Python application using our flatten PDF API.
You can integrate these functions into your existing applications and flatten PDFs. With the same API token, you can also perform other operations, such as merging documents into a single PDF, adding watermarks, and more. To get started with a free trial, sign up(opens in a new tab) here.
FAQ
Flattening merges all interactive and layered elements (form fields, annotations, signatures, transparency) into a single static layer. The resulting PDF appears identical but can no longer be edited — all content becomes part of the base document layer.
No. Flattening is a permanent operation. Once a PDF is flattened, you cannot restore the original editable form fields or layered annotations. Always keep a backup of your original document before flattening.
Flattening typically reduces file size slightly because it removes interactive layer data and form field metadata. However, the visual appearance remains identical to the original document.
The free account includes 200 credits. Each flatten operation consumes 0.5 credits, regardless of file size. This means you can flatten up to 400 PDFs with your free account. You can also combine flattening with other operations (like merging or watermarking) in a single API call.
Yes. However, you’ll need to provide the password during the API call. The Nutrient API supports processing password-protected PDFs when proper credentials are included in the request.
The API accepts PDF files. If you need to flatten form fields in other formats (like Word documents with forms), you can first convert them to PDF and then apply flattening in a single API operation.






