Convert HTML to PDF in JavaScript with html2pdf.js
Table of contents

html2pdf.js is a lightweight JavaScript library that converts HTML to PDF entirely on the client side by combining html2canvas(opens in a new tab) (for capturing HTML elements) and jsPDF (for PDF generation). It requires minimal setup — just include the library, select your HTML element, configure options like page size and margins, and call html2pdf().from(element).save(). It’s great for simple documents, but for complex layouts or advanced features, consider Nutrient’s HTML-to-PDF API.
Why choose html2pdf.js?
html2pdf.js offers an easy and efficient way to generate PDFs directly in the browser:
- Runs entirely in the browser — No server needed; great for privacy and speed.
- Simple API — Include the library, select an element, and call
.save(). - Customizable output — Set margins, page size, orientation, and image quality.
If you’re building lightweight tools, invoices, or downloads from HTML content, it’s a quick win.
Getting started with html2pdf
- First, you’ll need to include html2pdf.js in your HTML file. You can do this by either downloading the library from the official GitHub repository(opens in a new tab) or including it via a content delivery network (CDN)(opens in a new tab):
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/html2pdf.js/0.10.2/html2pdf.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha512-MpDFIChbcXl2QgipQrt1VcPHMldRILetapBl5MPCA9Y8r7qvlwx1/Mc9hNTzY+kS5kX6PdoDq41ws1HiVNLdZA==" crossorigin="anonymous" referrerpolicy="no-referrer"></script>Now that you’ve included the library in your project, follow the next steps to convert your HTML content to PDF.
- Create the HTML content you want to convert to a PDF file. You can either use an existing HTML element on your webpage or create a new one. For this example, you’ll create a
<div>containing some text and basic styling:
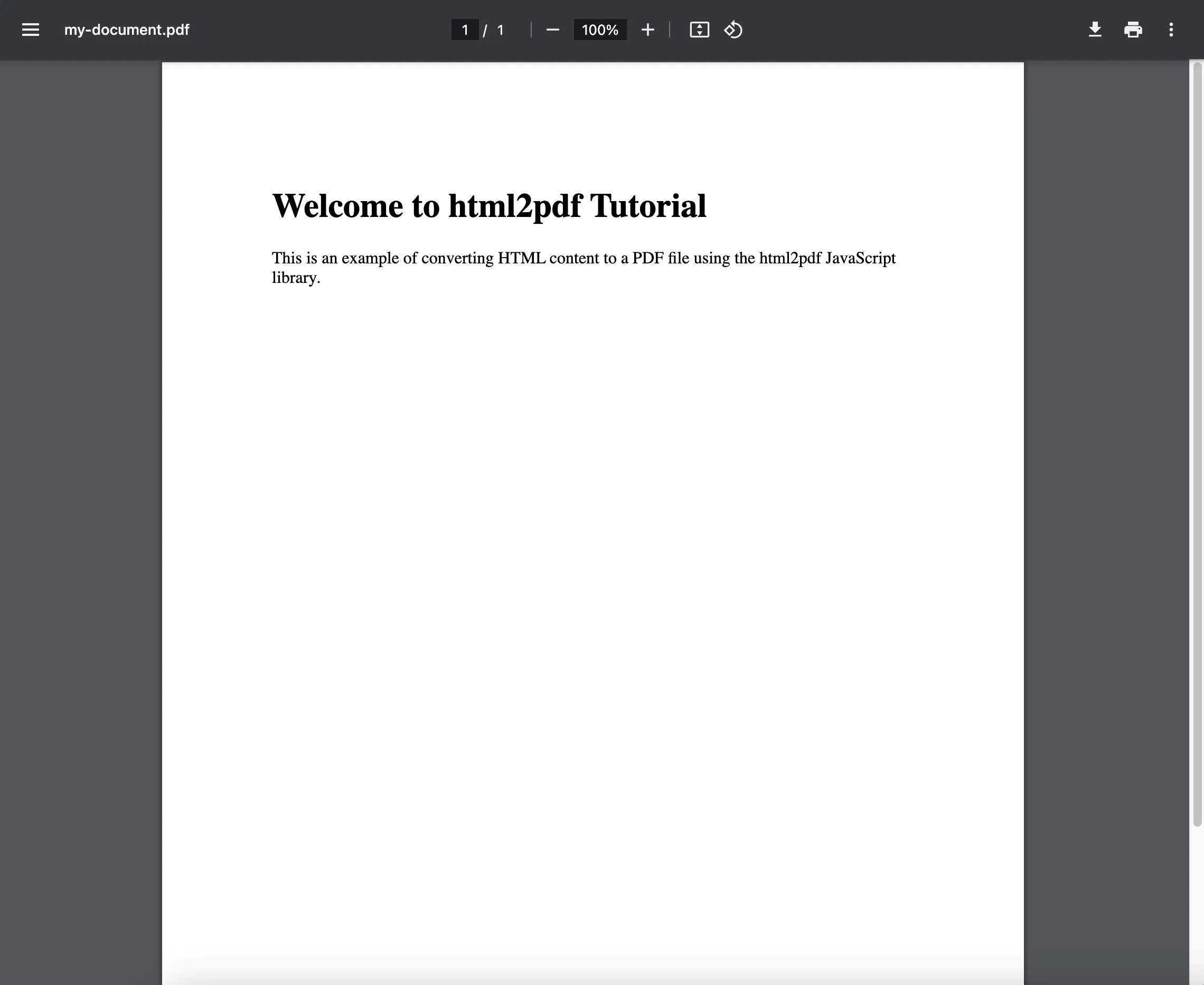
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <title>HTML to PDF Using html2pdf</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" /> <!-- html2pdf CDN link --> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/html2pdf.js/0.10.2/html2pdf.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha512-MpDFIChbcXl2QgipQrt1VcPHMldRILetapBl5MPCA9Y8r7qvlwx1/Mc9hNTzY+kS5kX6PdoDq41ws1HiVNLdZA==" crossorigin="anonymous" referrerpolicy="no-referrer" ></script> </head> <body> <div id="content"> <h1 id="my-element">Welcome to html2pdf Tutorial</h1> <p> This is an example of converting HTML content to a PDF file using the html2pdf JavaScript library. </p> </div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body></html>- Create a JavaScript file (e.g.
index.js). Select the HTML element(s) you want to convert to PDF. This can be done using JavaScript DOM selectors. For example, if you want to convert the entire webpage, you can select thedocument.documentElement(opens in a new tab) property, which represents the root element of the HTML document:
const element = document.documentElement;This will select the <html> element and all of its children, including the <head> and <body> elements, to be converted to PDF. If you only want to convert a specific part of the page, you can select a different element using a CSS selector, such as an ID or class name, like this:
const element = document.querySelector('#my-element');This would select the element with the ID my-element to be converted to PDF.
- After selecting your HTML element(s), you can specify the conversion options you want to use. Some of the available options include the file name, paper size, page orientation, margins, and image quality. Here’s an example:
const options = { filename: 'my-document.pdf', margin: 1, image: { type: 'jpeg', quality: 0.98 }, html2canvas: { scale: 2 }, jsPDF: { unit: 'in', format: 'letter', orientation: 'portrait' },};In this example, you’re specifying that you want the PDF to be named 'my-document.pdf', and you want to use JPEG images with 98 percent quality. You’re also setting some options for html2canvas and jsPDF. Note that you can customize these options to suit your needs.
- Finally, you can use the
html2pdf()function to initiate the conversion and save the resulting PDF:
html2pdf().set(options).from(element).save();In this example, you’re using the set() method to configure the conversion options, the from() method to specify the HTML element(s) to convert, and the save() method to save the PDF file.
- Open the HTML file in a browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge. This will download the PDF file to your computer.
Customization examples
html2pdf.js lets you customize the PDF output to suit your needs. Below are some examples of how to adjust the PDF settings.
- Example 1: Set page size and orientation
Choose from standard page sizes (e.g. A4, letter) and set the orientation (portrait or landscape):
const options = { jsPDF: { unit: 'mm', format: 'a4', orientation: 'landscape' },};- Example 2: Add headers and footers
const options = { jsPDF: { unit: 'in', format: 'letter', orientation: 'portrait' }, pagebreak: { mode: 'avoid-all', before: '#page2el' },};html2pdf.js provides many more configuration options(opens in a new tab) and customization features that you can explore in its documentation.
Performance considerations and limitations
1. Handling large content
Converting large or complex HTML content can be resource-intensive. To optimize performance:
- Break content into smaller sections.
- Use pagination to split content across multiple pages.
- Avoid excessive use of high-resolution images.
2. Browser compatibility
html2pdf.js is compatible with most modern browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. However, some older browsers may not fully support its features. Always test your implementation across different browsers to ensure compatibility.
3. Limitations
While html2pdf.js is a powerful tool, it has some limitations:
- CSS and JavaScript rendering — Certain CSS styles and JavaScript-driven content may not render accurately.
- Advanced PDF features — Features like embedded fonts, annotations, and form fields aren’t supported.
- Performance issues — Large documents may take longer to process and can strain system resources.
Alternatives to html2pdf.js
While html2pdf.js is a popular option for converting HTML to PDF, there are several other libraries and tools available for this purpose. Below are some of the alternatives to consider.
- wkhtmltopdf — This is a command-line tool that uses the WebKit rendering engine to convert HTML to PDF. It supports advanced features such as headers and footers, tables of contents, and page numbering. However, it requires server-side processing and may not be as customizable as html2pdf.js. Check out the How to convert HTML to PDF in C# using wkhtmltopdf blog post for more information.
- Puppeteer — This is a Node.js library that provides a high-level API for controlling headless Chrome or Chromium browsers. It can be used to generate PDFs from HTML content, and it supports advanced features such as page breaks, headers and footers, and tables of contents. However, it requires server-side processing and may not be as lightweight as html2pdf.js. Check out the top JavaScript PDF libraries blog post for more information.
- Nutrient — Nutrient offers several ways to convert HTML to PDF across different platforms and frameworks. The next section outlines the main approaches.
Using Nutrient PDF generation API
Nutrient PDF generation API allows you to convert HTML and CSS templates into secure, production-quality PDF documents. Benefits include:
- SOC 2 compliance for data security
- REST API with clear documentation and code samples
- Access to 30+ PDF tools (merge, compress, watermark, and more)
- Transparent, pay-as-you-go pricing
Start with 200 free credits(opens in a new tab) — no commitment required.
Using Document Engine
Need full design control? Document Engine lets you build PDFs from HTML/CSS with:
- Pixel-perfect layout control
- Form support, templates, image conversion
- Server-side deployment for complete customization
Platform-specific options
Android
The HtmlToPdfConverter class supports:
- HTML- or URL-to-PDF conversion
- JavaScript rendering support
- Page size customization
- Progress monitoring
C# integration
To create a PDF from an HTML file using Nutrient’s SDK:
- Create a
GdPictureDocumentConverterobject. - Load the HTML file using
LoadFromFile, specifying the format. - Export to PDF using
SaveAsPDF.
using GdPictureDocumentConverter gdpictureDocumentConverter = new GdPictureDocumentConverter();// Load the source document.gdpictureDocumentConverter.LoadFromFile(@"C:\temp\source.html", GdPicture14.DocumentFormat.DocumentFormatHTML);// Save the output in a new PDF document.gdpictureDocumentConverter.SaveAsPDF(@"C:\temp\output.pdf");No-code (Zapier/Power Automate)
Automate HTML-to-PDF generation without writing code using:
- A Zapier integration
- Power Automate for Microsoft users
Nutrient’s solutions are regularly maintained, with releases occurring multiple times throughout the year. We also offer one-on-one support to handle any issues or challenges you encounter, which can be a significant advantage compared to open source solutions.
If you’re interested in Nutrient, you can contact our Sales team.
Conclusion
html2pdf.js is a fast, easy way to convert HTML to PDF directly in the browser with no server required. It’s perfect for simple use cases like invoices or reports. For more advanced features or large-scale needs, consider server-side tools or APIs like Nutrient. Start simple, and scale as your requirements grow.
FAQ
html2pdf.js is a client-side JavaScript library for converting HTML to PDF. It uses html2canvas to render the page as an image and jsPDF to create a downloadable PDF file — no server needed.
Include it via CDN or install it with npm install html2pdf.js. Then call html2pdf().from(element).set(options).save() to convert an HTML element into a PDF with optional customization.
Yes. You can configure filename, page size, margins, orientation, image type/quality, and more using the set() method and options like jsPDF and html2canvas settings.
It can struggle with large documents, dynamic or script-generated content, and complex CSS layouts. Since rendering is image-based, output may lose fidelity or appear blurry on high-resolution screens.
Nutrient offers HTML-to-PDF generation through a cloud API, SDKs, and no-code tools. Unlike html2pdf.js, Nutrient supports server-side rendering, pixel-perfect layouts, embedded fonts, forms, and enterprise features like security and compliance.
Use html2pdf.js for fast, simple, client-side exports. Choose Nutrient when you need high fidelity, support for large documents, automation (via Zapier/Power Automate), or production-grade PDF output with full customization and backend integration.